Procedures
Laparoscopic Surgeries
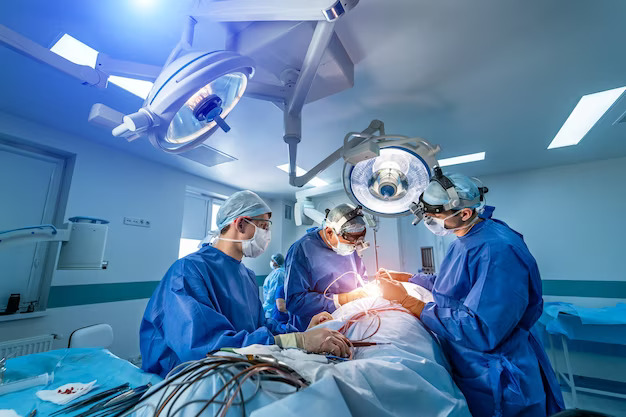
Laparoscopic Surgery: The Modern, Less Painful Alternative to Traditional Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, often called minimally invasive surgery, offers numerous benefits over traditional surgical methods. By utilizing small incisions and a laparoscope (a tiny camera), this technique ensures less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times. Patients experience shorter hospital stays, a lower risk of infection, and can return to daily activities much faster. Discover why laparoscopic surgery is becoming the preferred choice for many procedures, providing a precise and effective solution with significantly fewer drawbacks than traditional surgery.
Hernia Surgery & Repair
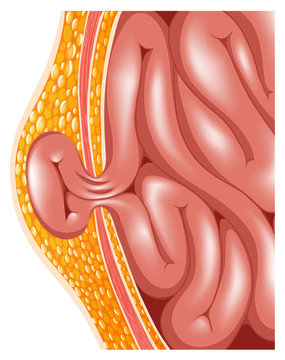
Understanding Hernias and the Importance of Timely Treatment
A hernia is a condition where an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the muscles, commonly occurring in the abdomen, groin, or upper thigh. Treating a hernia promptly is crucial to prevent complications such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off, leading to severe health risks. Early treatment alleviates pain and discomfort, prevents the hernia from enlarging, and helps you maintain your normal lifestyle. Addressing a hernia before it becomes an emergency situation ensures a smoother recovery and reduces the risk of serious complications.
Gallbladder Treatment
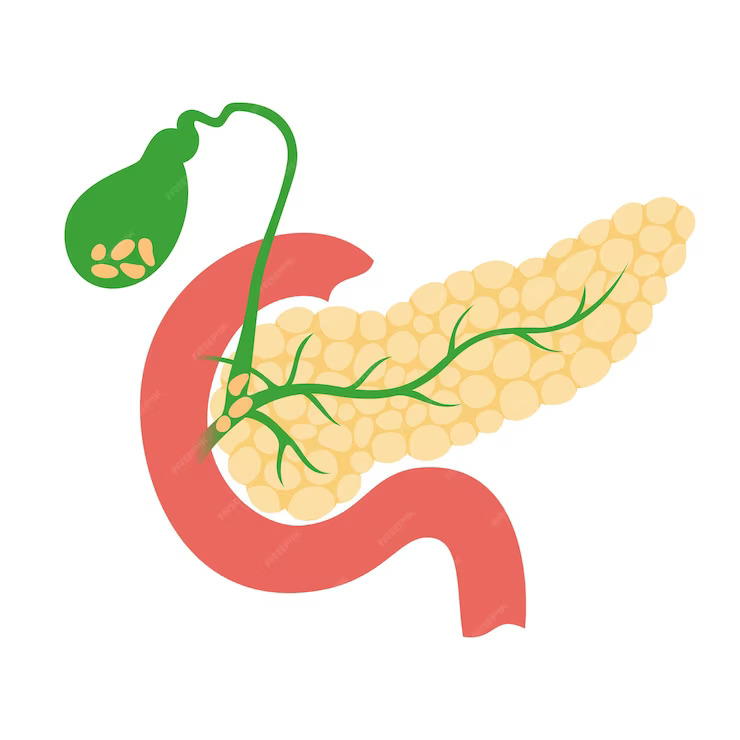
The Importance of Gallbladder Treatment and How It’s Done
Treating gallbladder problems is crucial to prevent severe pain, infections, and life-threatening complications. Common issues like gallstones or inflammation can disrupt digestive health and lead to significant discomfort. Early treatment not only alleviates pain but also prevents recurring issues and maintains digestive function.
How is Gallbladder Treatment Done? Depending on the severity, treatments range from medications and dietary changes to nonsurgical procedures. The most common and effective treatment is laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a minimally invasive surgery that removes the gallbladder through small incisions. This method offers a shorter recovery time and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery. Other options include endoscopic procedures to remove stones or relieve bile duct blockages. Seek timely medical advice to ensure effective treatment and maintain overall health.
Piles treatment
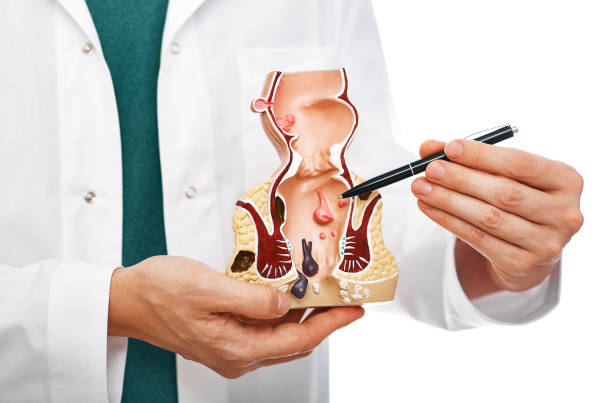
Understanding Piles and Their Treatment Options
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the rectum and anus causing pain, itching, and bleeding. Common causes include straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, obesity, and pregnancy. Symptoms range from discomfort and itching to swelling and bleeding during bowel movements.
Treatment for Piles varies based on severity:
Lifestyle and Home Remedies: Adopt a high-fiber diet, stay hydrated, take warm baths, and use over-the-counter creams to relieve symptoms.
Medications: Pain relievers and stool softeners can help manage symptoms.
Non-Surgical Procedures: Options like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, and coagulation therapy effectively shrink hemorrhoids.
Surgical Procedures: Hemorrhoidectomy and hemorrhoid stapling are available for severe cases, offering long-term relief.
Urology
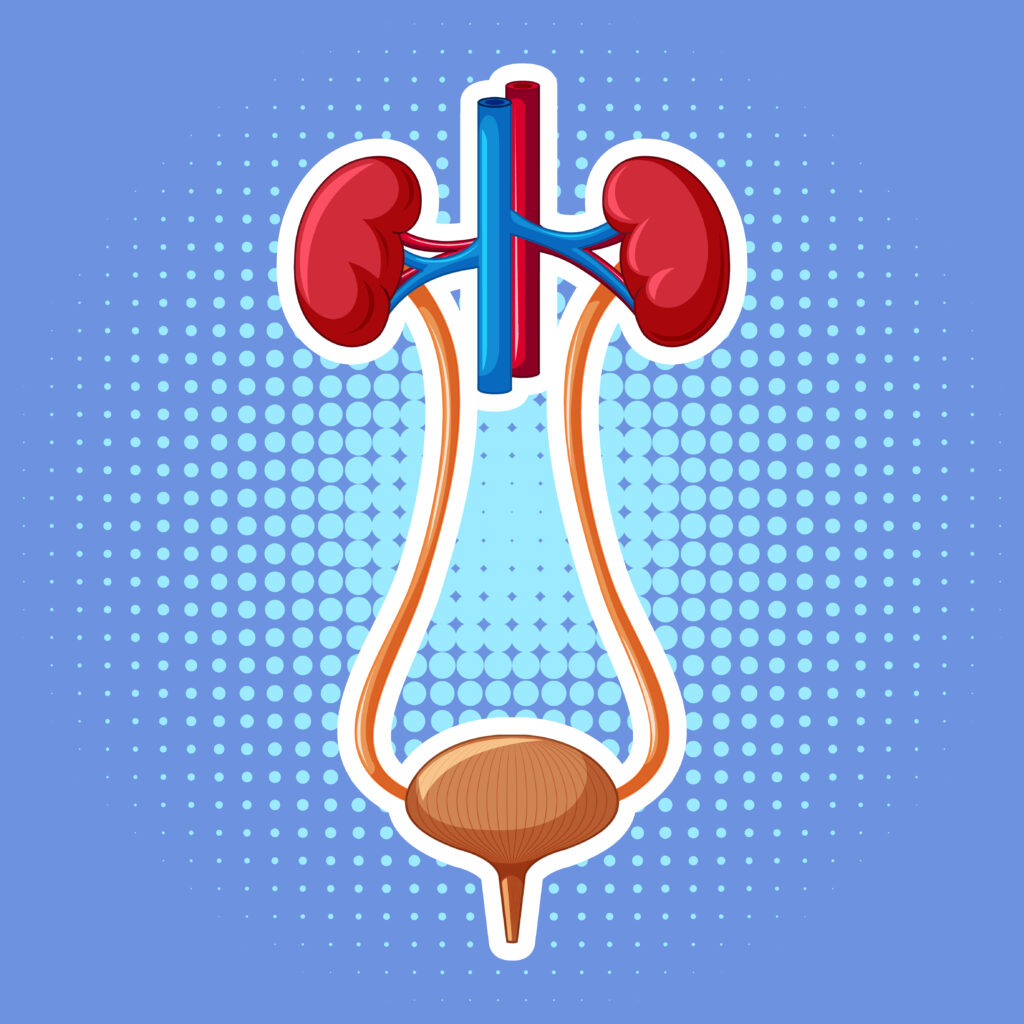

What is Urology?
Urology is a medical specialty dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of urinary system disorders and male reproductive organ issues. Key areas include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, prostate, testes, and penis. Urologists treat conditions such as UTIs, kidney stones, BPH, incontinence, erectile dysfunction, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, interstitial cystitis, and male infertility. Effective urological treatment is crucial for maintaining urinary and reproductive health, preventing complications, improving quality of life, and ensuring early detection and management of cancers. Consult a urologist for personalized care and treatment options.
Gastrointestinal Surgeries
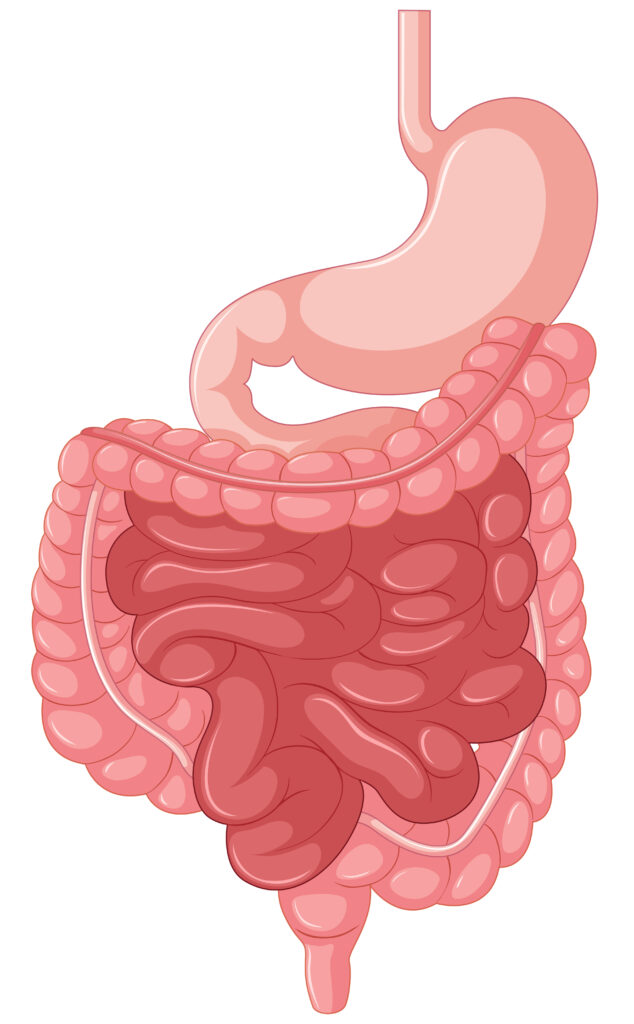
Gastrointestinal (GI) surgery involves surgical procedures on the digestive tract organs, including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and bile ducts. Common GI surgeries include:
- Appendectomy: Removes the appendix due to appendicitis.
- Cholecystectomy: Removes the gallbladder for gallstones or disease.
- Colectomy: Removes part or all of the colon for cancer or IBD.
- Gastrectomy: Removes part or all of the stomach for cancer or ulcers.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Removes severe hemorrhoids.
- Hernia Repair: Fixes various types of hernias.
- Liver Resection: Removes a portion of the liver for cancer or tumors.
- Pancreatectomy: Removes part or all of the pancreas for cancer or cysts.
- Small Bowel Resection: Removes a portion of the small intestine for cancer or Crohn’s disease.
- Whipple Procedure: Removes parts of the pancreas, small intestine, gallbladder, and bile duct for cancer.
- Esophagectomy: Removes part or all of the esophagus for cancer.
- Bariatric Surgery: Includes procedures like gastric bypass to treat obesity.
- Colostomy/Ileostomy: Creates a stoma to divert waste for bowel disease or injury.
- Anti-Reflux Surgery: Treats severe GERD not responding to medication.